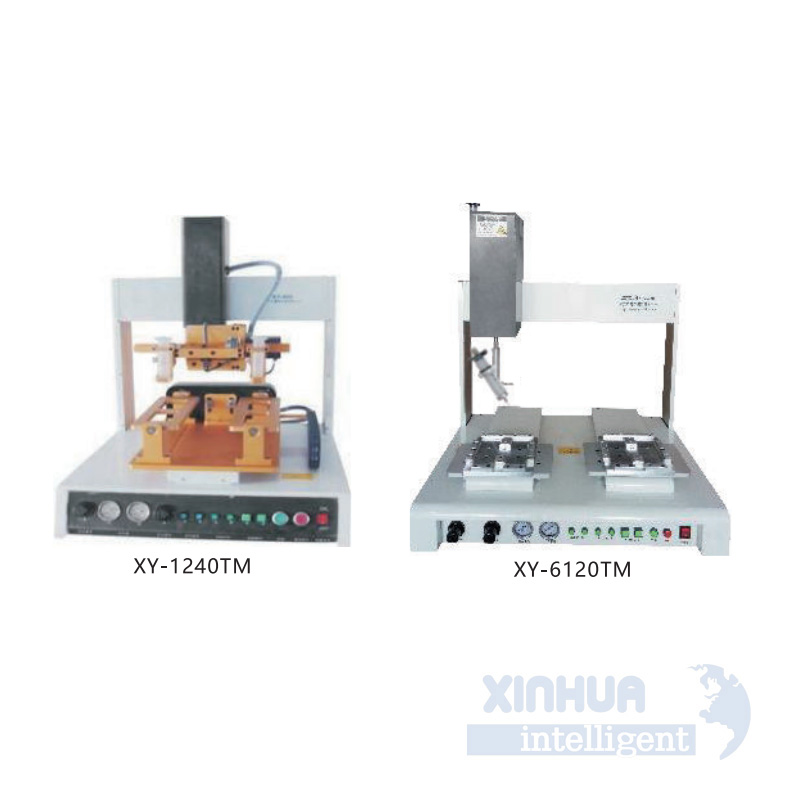

Maximizing Efficiency: Solving Challenges with Automatic Assembly Line Screw Machines
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, precision and efficiency are non-negotiable. One of the critical components in modern assembly lines is the automatic screw machine, a device that automates the process of screw feeding, driving, and torque control. These machines have become essential in industries ranging from automotive to electronics, where manual screwing would be too slow or error-prone.
However, despite their benefits, automatic screw machines come with their own set of challenges. In this article, we will explore the most common pain points manufacturers face when using these systems, discuss practical and technical solutions to overcome them, provide real-world applications across various industries, and conclude with insights on how partnering with a trusted provider like Xinhua Intelligent can elevate your production capabilities.
—
1. Common Pain Points and Challenges
While automatic screw machines significantly enhance productivity and reduce labor costs, they also introduce several operational and technical hurdles that need to be addressed for optimal performance.
A. Misfeeding and Jamming
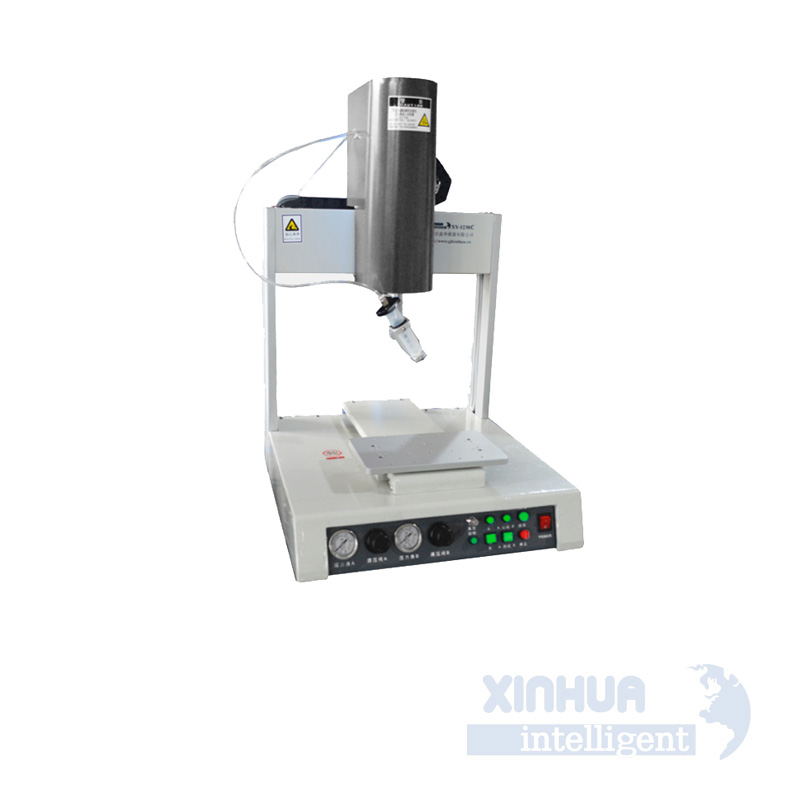

One of the most frequent issues encountered in automatic screw feeding systems is misfeeding—where screws fail to align properly in the track or get stuck during transport. This can cause delays, machine downtime, and even damage to downstream components if not detected early.
B. Torque Inconsistency
Torque accuracy is crucial in many applications, especially in safety-critical sectors such as aerospace or medical devices. Variations in torque settings due to tool wear, calibration drift, or inconsistent screw quality can lead to under-tightened or over-tightened joints, compromising product integrity.
C. Integration Complexity
Automatic screw machines often need to integrate seamlessly into existing automation systems, including robotic arms, conveyors, and PLC-based controllers. Compatibility issues between different brands or generations of equipment can complicate installation and maintenance.
D. High Initial Investment and ROI Concerns
While automation reduces long-term labor costs, the upfront investment in automatic screw machines—including hardware, software, and training—can be substantial. Many companies struggle to justify the cost without clear ROI projections or scalable deployment strategies.
E. Maintenance and Downtime
Regular maintenance is required to ensure consistent performance. However, unplanned downtime for repairs or part replacement can disrupt production schedules and impact delivery timelines.
—
2. Practical and Technical Solutions
To address these challenges effectively, manufacturers must adopt both technological advancements and best practices in system design and operation.
A. Advanced Feeding Systems
Modern automatic screw machines now incorporate vibratory bowl feeders and linear track systems equipped with sensors to detect and correct misaligned screws in real time. Some models use vacuum-assisted picking or magnetic alignment to improve reliability.
Additionally, AI-powered vision systems can identify orientation errors before screws are picked up by the driver, reducing jamming and increasing uptime.
B. Closed-Loop Torque Control
To maintain precise torque application, leading manufacturers are adopting closed-loop servo-driven screwdrivers. These systems continuously monitor torque and angle feedback, adjusting in real time to compensate for variations in screw material, thread condition, or driver wear.
Integrated data logging and traceability features allow manufacturers to audit each screwing cycle, which is particularly valuable in regulated industries.
C. Modular and Scalable Design
To ease integration, newer automatic screw machines are built with modular architectures that support plug-and-play compatibility with common industrial communication protocols such as EtherCAT, PROFINET, and Modbus TCP. This allows seamless connection to MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and SCADA platforms.
Furthermore, standardized interfaces and pre-configured modules enable faster deployment and easier scaling across multiple production lines.
D. Cost Optimization Strategies
To mitigate high initial costs, companies can opt for phased implementation, starting with pilot projects in high-volume or high-complexity stations. Using cloud-based analytics and predictive maintenance tools can also help reduce lifecycle costs by extending machine longevity and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Some providers offer leasing or pay-per-use models, allowing smaller manufacturers to access advanced automation without large capital expenditures.
E. Predictive Maintenance and Remote Diagnostics
By embedding IoT-enabled sensors and connectivity, modern automatic screw machines can transmit performance data to centralized monitoring systems. This enables predictive maintenance, identifying potential failures before they occur and scheduling service during planned downtime.

Remote diagnostics via mobile apps or web portals further streamline troubleshooting and reduce reliance on on-site technicians.
—
3. Real-World Applications
The versatility of automatic screw machines makes them indispensable across a wide range of industries. Below are a few notable examples:
A. Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive assembly plants, automatic screw machines are used extensively in powertrain, chassis, and interior component assembly. For instance, electric vehicle battery packs require hundreds of screws to be tightened with exact torque specifications to ensure structural integrity and electrical continuity.
Automated systems here not only improve speed but also ensure compliance with stringent safety standards.
B. Electronics Production
Consumer electronics manufacturing demands extremely high precision and miniaturization. Automatic screw machines are employed in assembling smartphones, laptops, and other devices where small screws (as tiny as M1.0) must be driven accurately and efficiently.
Vision-guided systems ensure that even micro-screws are placed correctly, preventing costly rework and improving yield rates.
C. Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, where failure is not an option, automatic screw machines are used to assemble avionics, landing gear components, and engine parts. These machines are integrated with traceability systems that log every screwing event, including torque values and timestamps, ensuring full compliance with FAA and ISO standards.
D. Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical devices such as surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment require sterile environments and strict adherence to quality controls. Automatic screw machines help maintain cleanroom conditions by reducing human intervention while ensuring repeatable, compliant assembly processes.
—
4. Conclusion: Elevate Your Production with Xinhua Intelligent
Automatic screw machines are no longer a luxury—they are a necessity for any manufacturer aiming to stay competitive in the era of Industry 4.0. While the challenges associated with these systems can seem daunting, the right combination of technology, strategy, and partner support can turn them into opportunities for growth and innovation.
Xinhua Intelligent stands at the forefront of automated screwing solutions, offering a comprehensive portfolio of smart, scalable, and high-precision automatic assembly line screw machines. With years of experience and a commitment to R&D, Xinhua delivers customized automation systems tailored to meet the unique needs of diverse industries.
Whether you’re looking to upgrade your current assembly line or implement a fully automated screwing solution from scratch, Xinhua Intelligent provides end-to-end support—from consultation and design to installation and ongoing service.
Contact Xinhua Intelligent today to schedule a consultation and discover how our intelligent screwing systems can transform your production floor. Let us help you achieve higher efficiency, better quality, and lower operational costs—every screw, every time.
—
Keywords: Automatic Assembly Line Screw Machine, Industrial Automation, Smart Manufacturing, Precision Torque Control, Xinhua Intelligent, Automated Screw Driving, Manufacturing Efficiency, Industry 4.0, Robotics Integration, Predictive Maintenance.
