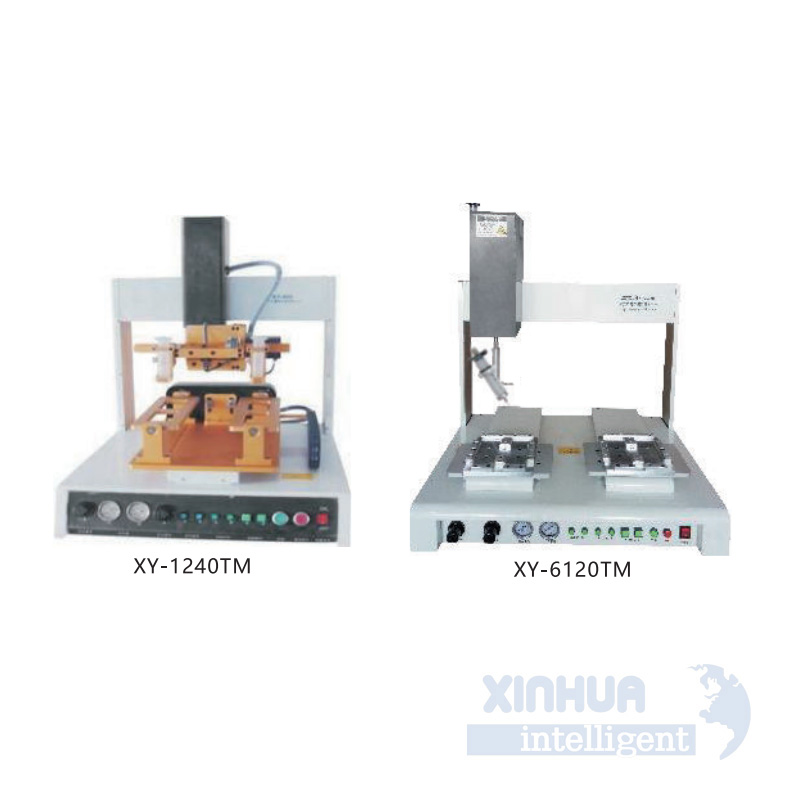

Title: Enhancing Efficiency and Precision with Desktop Screw Driving Machines
In the modern manufacturing landscape, efficiency, precision, and consistency are not just buzzwords—they are essential components of operational success. One tool that has emerged as a game-changer in this pursuit is the desktop screw driving machine. Designed for small to medium-scale assembly operations, these compact yet powerful devices offer automated screw insertion and tightening solutions that significantly reduce manual labor, improve product quality, and streamline production processes.
However, despite their benefits, many manufacturers still rely on manual screwdriving or outdated tools due to misconceptions about cost, complexity, or integration challenges. In this article, we will explore the common pain points associated with traditional screwdriving methods, discuss practical and technical solutions offered by desktop screw driving machines, examine real-world applications across industries, and conclude with a call to action for professionals looking to adopt this technology.
—
1. Common Pain Points or Challenges
A. Labor Intensity and Human Error
Manual screwdriving remains a widespread practice, especially among smaller manufacturers or those operating under tight budgets. However, this method comes with significant drawbacks. Repetitive screwdriving tasks can lead to worker fatigue, which increases the likelihood of errors such as missed screws, cross-threading, or inconsistent torque application. These mistakes not only affect product quality but also result in costly rework or warranty claims.

B. Inconsistent Torque Application
Achieving consistent torque is critical in many industries—particularly electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. Manual screwdrivers lack the ability to precisely control torque, leading to either under-tightened or over-tightened fastenings. Over time, this inconsistency can compromise product reliability and safety.
C. Lack of Data Tracking and Process Control
Traditional screwdriving methods typically do not support data logging or process monitoring. Without real-time feedback, it’s difficult to track performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, or ensure compliance with quality standards like ISO 9001. This absence of traceability can be a major liability during audits or recalls.
D. Low Throughput and Bottlenecks
Manual assembly lines often suffer from slow cycle times due to the limitations of human speed and endurance. As demand increases, scaling up with additional labor becomes expensive and inefficient. Furthermore, integrating automation into existing workflows without disrupting current operations can seem daunting.
—
2. Practical and Technical Solutions
To address these challenges, manufacturers are increasingly turning to desktop screw driving machines, which combine automation, precision engineering, and smart technology to deliver superior results.
A. Automated Screw Feeding and Driving
Modern desktop screw driving machines come equipped with automatic screw feeding systems that eliminate the need for manual handling. Screws are fed through a vibration bowl or linear feeder directly to the driver unit, reducing idle time and minimizing the risk of missing or misaligned screws.
These machines use programmable drivers that can apply precise torque values tailored to specific applications. Some advanced models even feature closed-loop torque control, ensuring that each screw is tightened to exact specifications every time.
B. Integrated Quality Control Features
Many desktop screw driving machines include built-in sensors and software that monitor each screwdriving operation in real time. If a fault occurs—such as a stripped screw, incomplete seating, or incorrect torque—the system can automatically flag the issue and halt further processing until the problem is resolved.
Additionally, some machines support data logging and connectivity via Ethernet or USB, allowing manufacturers to collect detailed records of each operation. This data can be used for statistical process control (SPC), root cause analysis, and audit preparation.
C. Compact Design and Easy Integration
Despite their advanced capabilities, desktop screw driving machines are designed to fit seamlessly into existing workstations. Their compact footprint makes them ideal for benchtop use, and most units can be integrated with minimal changes to current workflows.
Furthermore, user-friendly interfaces allow operators to quickly set up jobs, adjust parameters, and switch between different screw types or configurations without extensive training.

D. Scalability and Flexibility
For manufacturers seeking to scale their operations, desktop screw driving machines offer modular designs that can be expanded with additional axes, multi-spindle heads, or robotic arms. This flexibility allows companies to adapt to changing production needs without investing in entirely new systems.
Some models also support multi-axis motion control, enabling complex screw patterns and angled installations that would be difficult to achieve manually.
—
3. Real-World Applications
The versatility of desktop screw driving machines makes them suitable for a wide range of industries and applications. Below are a few notable examples:
A. Electronics Manufacturing
In the electronics sector, where miniaturization and precision are paramount, desktop screw driving machines are used to assemble smartphones, laptops, PCBs, and other sensitive components. These machines ensure that tiny screws are driven accurately without damaging surrounding circuitry or causing micro-fractures.
B. Automotive Component Assembly
Automotive suppliers use desktop screw driving machines to assemble interior panels, sensors, connectors, and control modules. The ability to maintain consistent torque is crucial here, as loose or overtightened fasteners can lead to component failure or safety hazards.
C. Medical Device Production
Medical device manufacturers require stringent quality control and regulatory compliance. Desktop screw driving machines provide the precision and traceability needed to meet FDA and ISO standards. They are commonly used in assembling surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and wearable health monitors.
D. Consumer Goods and Appliance Manufacturing
From assembling vacuum cleaners to kitchen appliances, desktop screw driving machines help consumer goods manufacturers maintain high output levels while ensuring product durability. The machines’ ability to handle multiple screw sizes and drive types makes them ideal for diverse product lines.
E. Aerospace and Defense
In these highly regulated industries, even minor assembly flaws can have serious consequences. Desktop screw driving machines are employed to build avionics, control boxes, and structural components, where repeatability and documentation are non-negotiable.
—
4. Conclusion and Call to Action
As manufacturing continues to evolve, so too must the tools that power its operations. Desktop screw driving machines represent a powerful blend of automation, precision, and intelligence that can transform the way products are assembled. By addressing common pain points such as labor intensity, inconsistent torque, and poor traceability, these machines enable manufacturers to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve overall product quality.
Whether you’re managing a small electronics workshop or overseeing a mid-sized production line, adopting a desktop screw driving machine is a strategic investment that pays dividends in both the short and long term.
If you’re ready to take your assembly process to the next level, consider partnering with Xinhua Intelligent, a leader in intelligent automation solutions. With a wide range of desktop screw driving machines tailored to various industrial needs, Xinhua Intelligent offers cutting-edge technology, reliable support, and customized integration services to help you achieve optimal performance.
Visit [www.xinhuai.com](http://www.xinhuai.com) today to explore our product lineup, request a demo, or speak with one of our automation experts. Let us help you drive innovation—and screws—with precision.
—
Keywords: desktop screw driving machine, automated screwdriver, precision assembly, manufacturing automation, Xinhua Intelligent.
