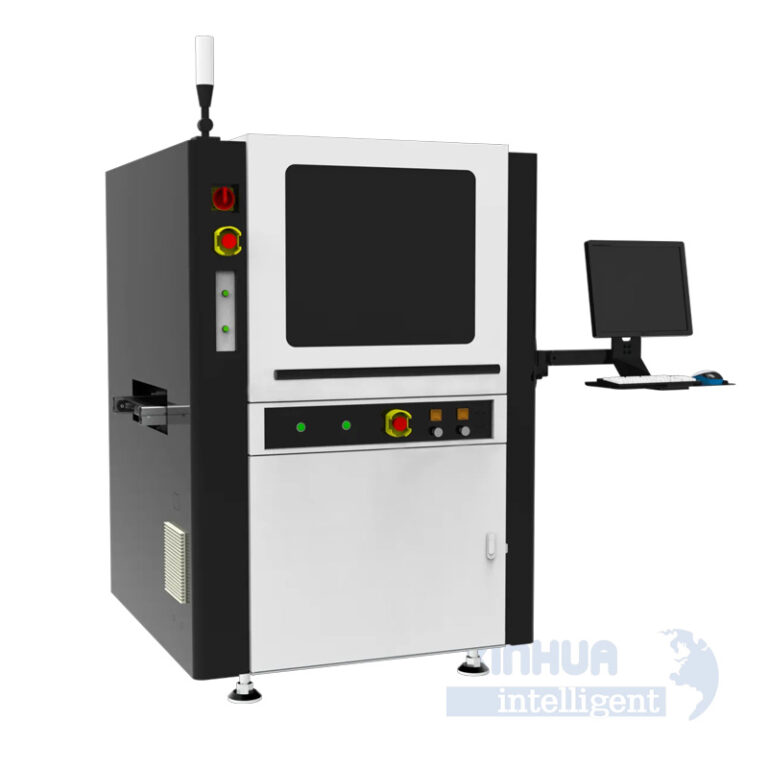

The Rise of Precision and Efficiency: Understanding Automatic Screw Tightening Machines
In the modern manufacturing landscape, precision, speed, and consistency are not just desirable—they’re essential. As industries evolve to meet higher production demands and stricter quality standards, automation becomes a critical component in maintaining competitive advantage. One area where automation has made significant strides is in screw tightening—a seemingly simple task that, when scaled across thousands of units per day, can become a major bottleneck if handled manually.
Automatic screw tightening machines have emerged as a game-changing solution for manufacturers looking to optimize their assembly lines. In this article, we will explore the common pain points associated with traditional screw tightening methods, examine the technical solutions provided by automatic systems, highlight real-world applications, and conclude with a look at how Xinhua Intelligent offers cutting-edge solutions tailored for industrial needs.
—
1. Common Pain Points or Challenges
Despite its ubiquity in manufacturing, manual screw tightening is fraught with challenges that can hinder productivity, compromise product quality, and increase operational costs. Here are some of the most pressing issues:
A. Human Error and Inconsistency
Manual screw tightening is highly dependent on operator skill and attention. Even experienced workers can make mistakes due to fatigue or distractions, leading to over-tightened, under-tightened, or missing screws. These inconsistencies can result in defective products, rework, or even safety hazards in critical applications like automotive or aerospace assemblies.
B. Low Throughput and Bottlenecks
Hand-tightening is inherently slow compared to automated processes. In high-volume production environments, manual operations can become bottlenecks that delay entire production lines. The time required to locate screws, align them correctly, and apply the proper torque adds up quickly, reducing overall line efficiency.
C. Ergonomic and Labor Issues
Repetitive screw tightening tasks can lead to ergonomic injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis among workers. Additionally, finding skilled labor willing to perform repetitive, low-value tasks is becoming increasingly difficult, especially in regions facing labor shortages.
D. Quality Control and Traceability
Ensuring consistent torque application and traceability across every fastening operation is challenging with manual methods. Without precise data tracking, identifying and addressing defects becomes more complex, which can affect compliance with industry standards and customer expectations.
—
2. Practical and Technical Solutions
Automatic screw tightening machines address these challenges through a combination of mechanical precision, intelligent control systems, and integration capabilities. Let’s explore how they overcome each pain point:
A. Precision Torque Control
Modern automatic screwdrivers come equipped with advanced torque control systems—often using closed-loop feedback mechanisms—that ensure each screw is tightened to exact specifications. These systems can adjust torque in real-time based on resistance, preventing over- or under-tightening and ensuring consistent joint integrity.
B. Integrated Feeding Systems
One of the key features of automatic screw tightening machines is the use of automated feeding systems. Vibratory bowl feeders, linear feeders, or flexible tube feeders supply screws directly to the tightening head, eliminating the need for manual handling. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces the chance of human error.
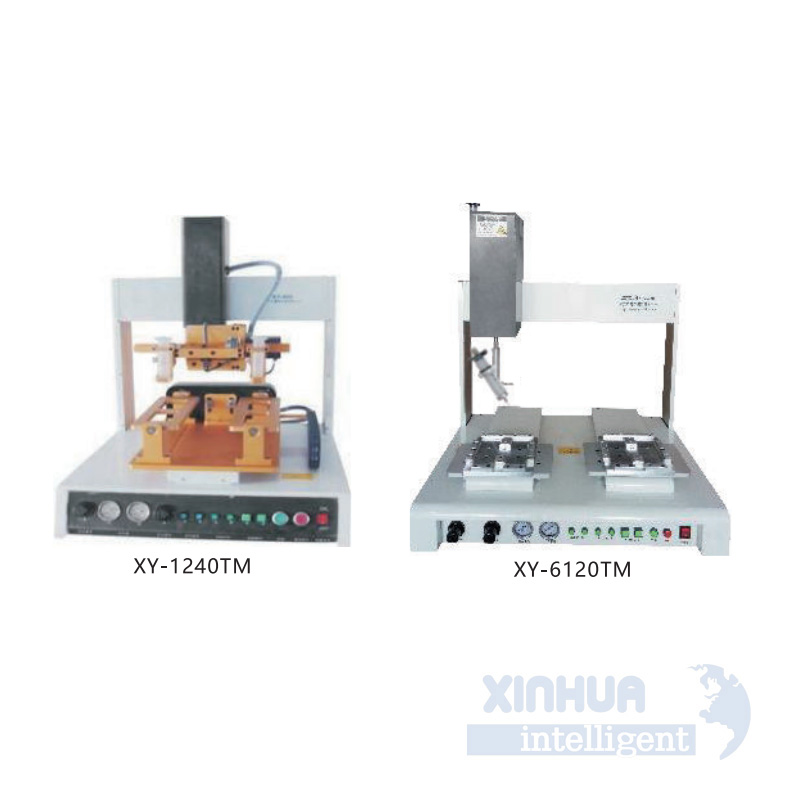
C. Multi-Axis and Robotic Integration
For complex assemblies requiring multiple screw locations, multi-axis screwdrivers or robotic arms can be programmed to follow precise paths and tighten screws in specific sequences. These systems can handle 3D geometries, tight spaces, and variable screw sizes—all while maintaining accuracy and repeatability.
D. Data Collection and Quality Assurance
Most automatic screw tightening machines today are equipped with IoT-enabled controllers that collect real-time data such as torque values, angle of rotation, pass/fail status, and timestamps. This data can be integrated into MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) or SCADA systems for full traceability, enabling predictive maintenance, root cause analysis, and compliance reporting.
E. Ergonomic and Labor Optimization
By automating repetitive tasks, companies can redeploy human workers to more value-added roles, improving job satisfaction and reducing workplace injuries. Automation also allows for 24/7 operation without fatigue-related errors, significantly boosting throughput.
—
3. Real-World Applications
Automatic screw tightening machines are now widely adopted across various industries where quality, speed, and reliability are paramount. Below are some notable examples:
A. Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive assembly plants, thousands of screws are used in everything from engine components to interior panels. Automatic screw tightening ensures that each joint meets strict torque specifications, contributing to vehicle safety and durability. Robots equipped with screwdrivers are often used in conjunction with conveyor systems to maintain continuous flow production.
B. Electronics Assembly
From smartphones to industrial control panels, electronics manufacturing requires extreme precision. Manual screwing in such delicate environments can damage sensitive components. Automatic systems ensure gentle yet accurate tightening, often with micro-torque settings down to 0.1 Nm.

C. Appliances and Consumer Goods
Major appliance manufacturers use automatic screw tightening machines to assemble washing machines, refrigerators, and HVAC units. These systems improve line efficiency and reduce rework rates, helping manufacturers scale production while maintaining quality.
D. Medical Device Manufacturing
In regulated industries like medical devices, traceability and compliance are non-negotiable. Automatic screw tightening machines log every fastening event, providing auditable records that meet ISO and FDA requirements. This level of control is crucial in life-critical applications.
E. Aerospace and Defense
High-reliability sectors such as aerospace demand zero-defect assembly practices. Automatic screw tightening machines ensure that fasteners in aircraft engines, avionics, and structural components are applied with absolute consistency, supporting mission-critical performance.
—
4. Conclusion: Elevate Your Production Line with Xinhua Intelligent

As we’ve seen, automatic screw tightening machines offer a robust solution to many of the inefficiencies and risks associated with manual assembly. By integrating advanced torque control, smart feeding systems, and data-driven monitoring, these machines empower manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision, throughput, and quality assurance.
Whether you’re assembling consumer electronics, automotive parts, or industrial machinery, investing in an automatic screw tightening system is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced market.
At Xinhua Intelligent, we specialize in delivering high-performance, customizable automatic screw tightening solutions designed to meet the evolving needs of modern manufacturing. Our systems combine cutting-edge technology with user-friendly interfaces, ensuring seamless integration into your existing production lines.
Ready to transform your assembly process? Contact Xinhua Intelligent today to schedule a consultation and discover how our automatic screw tightening machines can help you achieve smarter, faster, and more reliable production.
👉 [Contact Us Now]()
📞 +86 XXX-XXXXXXX
📧 sales@xinhua-intelligent.com
🌐 www.xinhua-intelligent.com
—
Tags: Automation ScrewTighteningMachine SmartManufacturing IndustrialAutomation AssemblyLineEfficiency XinhuaIntelligent
